Processes & Threads
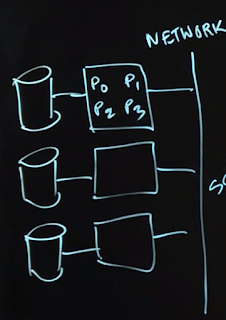
這是之前提過高階ABSTRACTION的底層JVM process,一個process可以創造多個threads,分享process的資源(記憶體)。對datacenter中的一個node來說,普遍一個node有16核心,一個process產生的一個thread可以使用一個核心的計算能力,所以單一thread並不能使用multicore能力。
如果一個process產生multithreads,當然有syncrhonization的壓力,但是有不少好處,包括responsiveness / performance / resource sharing等。
那為何不一個node就跑一個process + 多個threads就好? (某些node的確只有一個process,例如medical system)
因為一個process就是一個application program,通常不會一個電腦只跑一個application,光是OS就是一個application了。此外一個node上跑多個processes有他的好處:
首先可以多工(多個application),例如JVM需要garbage collection,這是一個獨立的process,而且當garbage collection發生的時候,會blocking。所以不能單獨只有一個process在JVM node上。
此外單一process的multithreading帶來的throughput 提升是有極限的:
超過一個小量 n (workload dependent)個threads之後,甚至效能會下降,因為synchroniation overhead超越了多執行續帶來的效益。而multi process沒有此限制,可以充分利用一個node中的所有cores,這提供了scalability。
最後multiprocess提供resilience,也就是容錯。當一個process掛點,另一個監測的process可以知道,然後啟動一個新的process來繼續原本掛點process的任務。
所以processes是 distributed computing的基本單位 (提供高度scalability within datacenter),而threads則是concurrency/parallelism的基本單位 (提供有限scalability within a node)。
Multithreaded Servers
server先建立一個server socket,然後在一個loop中等待request。以之前的socket programming file server assignment來說,就是那樣。 但是一次只能等一個request充分serve之後,才能接受下一個request。所以要在每一次聽到一個request之後,就new一個thread去handle request,這就是利用到了multithreading:
不過allocate resource for a thread是很大的overhead,所以要利用threadpool或是tasks來reuse thread instance。
MPI and Multithreading
之前提到的MPI架構只有single threaded,所以並沒有用到一個node上所有的cores:現在如果要充分利用cores,就使用multithread,master thread在 一個node上負責啟動MPI:
有可能有以下幾種threading modes:
1. funnel: 只有一個master thread
2. serialized: 多個threads但一次只有一個thread能進行MPI calls
3. multiple: 多個threads且可以同時有多個threads進行MPI calls,當然如果是non-blocking MPI,兩個thread不能wait for 同一個requests。
Distributed Actors
之前concurrent Java 課程提到過Actor pattern,習題作業也有一題利用Sieve of Eratosthenes 演算法來使用actors計算質數,主程式碼如下:public final class SieveActor extends Sieve {
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
* TODO Use the SieveActorActor class to calculate the number of primes <=
* limit in parallel. You might consider how you can model the Sieve of
* Eratosthenes as a pipeline of actors, each corresponding to a single
* prime number.
*/
public static int primesCount = 0;
public SieveActor() { primesCount = 0; }
@Override
public int countPrimes(final int limit) {
//multiple threads will enter this critical section
PCDP.finish(() -> {
final SieveActorActor actor = new SieveActorActor(2);
for (int i = 3; i <= limit; i+=2) //just send odd numbers, since multiples of 2 are aready filtered
actor.send(i);
actor.send(0);
});
return primesCount;
}
/**
* An actor class that helps implement the Sieve of Eratosthenes in
* parallel.
*/
public static final class SieveActorActor extends Actor {
/**
* Process a single message sent to this actor.
*
* TODO complete this method.
*
* @param msg Received message
*/
private SieveActorActor nextActor;
private final int localPrimeNumber;
public SieveActorActor(int prime) {
localPrimeNumber = prime;
primesCount+=1;
}
@Override
public void process(final Object msg) {
final int candidate = (Integer)msg;
if (candidate == 0) {
if (nextActor != null)
nextActor.send(0);
return;
}
boolean isMult = ((candidate % localPrimeNumber) == 0);
if (!isMult) {
if (nextActor == null)
nextActor = new SieveActorActor(candidate); //the first non-multiple, new = starts actor
else
nextActor.send(candidate);
}
}
}
}
上面是單一 node版本,現在要善用distributed programming的話,就要在remote node上面產生新的remote actor,以下的步驟必須達到:
1. 製作一個config file,寫入每個actor被哪一個node host
2. 要有能力create remote actor
3. 要有能力傳message給remote actor
4. 因為是跨node傳message,當然messages要是serialized
Distributed Reactive Programming
在pub-sub model,publisher可以主動push或是subscriber主動pull,reactive programming就是要利用async events來coordinate這樣的溝通,讓micro services可以更好的implement。JDK 9 提供Flow API來實作reactive streams spec。
略。